1. YOLOv5
YOLOv5 paper not published
more info in github repo https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
GitHub - ultralytics/yolov5: YOLOv5 🚀 in PyTorch > ONNX > CoreML > TFLite
YOLOv5 🚀 in PyTorch > ONNX > CoreML > TFLite. Contribute to ultralytics/yolov5 development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
1-1. Architecture and Code (최신 YOLO에서 크게 공유되는 구조)
YOLO와 같은 detector의 경우, (1) Backbone : extract features (2) Neck : mix features across scales (3) Head : output boxes/classes 로 구성되어 있다.
(1) Backbone : 특정 사진을 여러개의 유용한 feature map으로 변형한다
YOLOv5에서는 이를
- Conv + BN + activation(SiLU) : learn filter step
- Downsampling(stride 2 conv) : input tensor 의 H, W를 줄이면서 channel 수를 증가시킴
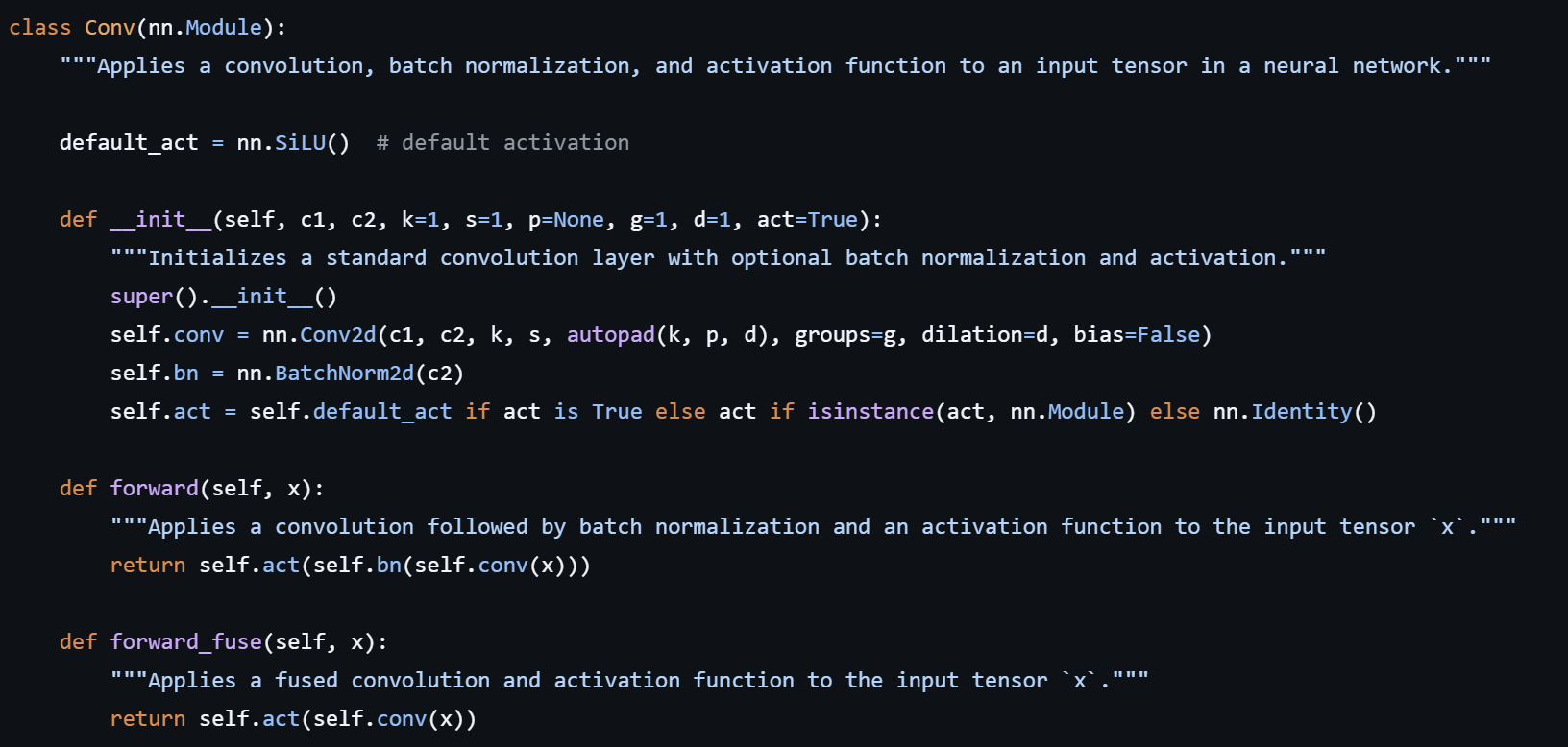
- CSP (Cross Stage Partial) / C3(CSP with 3 Convolutions
(YOLOv5's naming)) blocks : feature channel을 두개로 나눈후 하나는 heavy한 layers를 통과시키고 하나는 상대적으로 direct하게 유지시킨 후 다시 concatenate한다. (channel 차원은 1x1 convolution으로 맞춰줌) -> 이는 새롭게 정의한 autopad() 함수에서 실행됨

이때 신기했던 점은 c_ (hidden channels)을 정의할 때 c1 의 절반이 아니라 c2의 절반으로 했다는 점
(2) Neck : backbone의 여러가지 feature map들을 (diverse resolutions)들을 합쳐서 다양한 크기의 object을 detect할 수 있게 해준다.
(3) Head : 지금까지의 정보를 종합하여 detection과 classification을 수행함. (코드는 너무 길어서 사진 첨부 생략
전부 github에 공개 돼 있음)
1-2. Evolution of YOLO
- image를 SxS grid로 나눠서 detection과 classification을 진행함
- multi-scale training 을 추가하여 여러가지 resolutions을 활용할 수 있도록 함
- multi-scale detection heads를 추가하여 (3가지 zoom level) 다양한 크기의 object detection이 용이해짐
- neck에 SSP 추가 / PANet-style feature aggregation / Mosaic augmentation / CIoU Loss 등 다양한 training trick 추가
- SSP (Spatial Pyramid Pooling) : multiple window sizes to capture context
- PANet(Path Aggregation Net) : makes detection of multiple size objects easier (H W sizes are united through Upsampling) 이때 pixel resolution 정보는 H W 가 아닌 channel들에 저장돼 있기 때문에 Upsampling을 해도 그 정보를 해치지 않음!
- Mosaic augmentation : 모자이크 아님 주의 stitches 4 different input images into 1 (2x2)
- CIoU Loss : Overlap more + move the box center to the target

2. YOLOv9
YOLOv9 paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2402.13616
Ultralytics
2-0. Abstract
기존의 model들은 input data가 deep layer를 통과함에 따라서 information loss가 발생한다는 점을 간과하고 있음. 따라서 YOLOv9에서는 information bottleneck과 reversible functions를 통해 이를 해결하고자 함.
PGI (Progammable Gradient Information) 개념을 도입하여 deep network가 요구하는 다양한 변화를 활용하여 여러가지 목적을 달성할 수 있도록 했다.
GELAN (Generalized Efficient Layer Aggregation Network) 라는 gradient path planning 기반의 새로운 lightweight network architecture를 사용하여 lightweight model에서 PGI가 우월한 결과를 뽑아내도록 한다.
- 연구에서는 GELAN이 conventional convolution만을 이용하여 depthwise convolution을 활용한 state-of-the-art model 보다 좋은 성과를 낸다는 것을 보여줌
2-1. Information Bottleneck and Reversible functions
input data가 feedforward process 중 information loss가 발생하는 것을 information bottleneck라고 함.
하지만 이는 단순히 나쁜 현상이 아니다
operations가 너무 많은 것 또한 계산량 과부화가 발생하기 때문에 적절히 줄일 필요가 있음
따라서 3x3 convolution을 더 작은 H W 에서 하기 위해 이러한 과정을 선택

하지만 information loss가 발생하는 것은 사실이다.
이 information loss를 방지하기 위해 Reversible functions이 소개된다.
변환이 이상적으로 가역적이라면 충분히 손실된 정보를 복원할 수 있기 때문에 이를 활용하는 것이다.
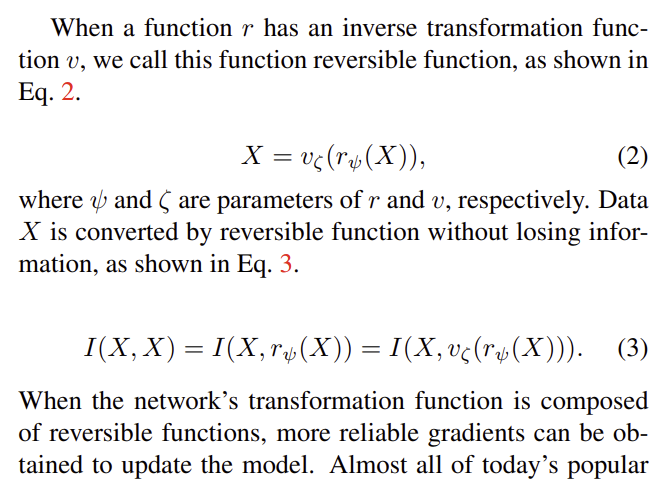
2-2. Progammable Gradient Information

Auxiliary Network designed to produce reliable gradients
- Main Branch : 기본적인 YOLO 구조와 동일
- Auxiliary Reversible Branch : reversible한 architecture를 이용해서 reliable한 gradients를 만들 수 있도록 한다.
(기존의 YOLO구조에서는 어느 특정 부분에 focus를 하게 될 경우 unreliable 한 gradients를 만들 가능성이 있었다) - Multi-level Auxiliary Information : integration network를 통해 다른 prediction head에서 온 gradients들을 종합한다.
이를 통해 target information을 가진 모든 gradient들을 aggregate 한 후에 main branch로 가져와서 parameter들을 업데이트한다.
이때 integration network는 returned gradients들을 more complete and less biased 하게 만들어줄 수 있기 때문에 존재함
2-3. GELAN (Generalized ELAN)
a combination of CSPNet and ELAN 로 등장한 새로운 network architecture
what is CSPNet / ELAN ?
- CSPNet (Cross Stage Partial Network) : YOLOv5에서도 등장한 CSP feature channel들을 2개로 나눈 후 한 부분만 heavy layer를 통과시킨 후 다시 concatenate 시키는 작업
- ELAN (Efficient Layer Aggregation Network): 여러가지의 sequential한 operation들이 있을 때 (conv stacks) 중간 단계들을 전부 concatenate시키는 것
What changes in GELAN ?
- 기존의 ELAN에서는 거의 convolution layer들의 stack만 활용하는 능력을 갖췄었지만 더 다양한 computational block을 사용할 수 있도록 generalize 한 것 (추가된 것들 중 CSP block이 존재함)
Where is GELAN used?
- Backbone과 feature extraction에 활용됨
2-4. Conclusion
PGI의 소개로 information bottleneck problem을 해결하고
GELAN이라는 lightweight neural network는 기존의 lighweight neural network가 deep supervision method에 적합하지 않은 점을 해결한다.

YOLOv9은 이 두가지를 합하여서 엄청난 성능을 자랑한다
3. YOLOv11
YOLOv11 paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2410.17725
Ultralytics
3-0. Abstract
YOLO계열 detector 의 가장 최신 버전인 YOLOv11은
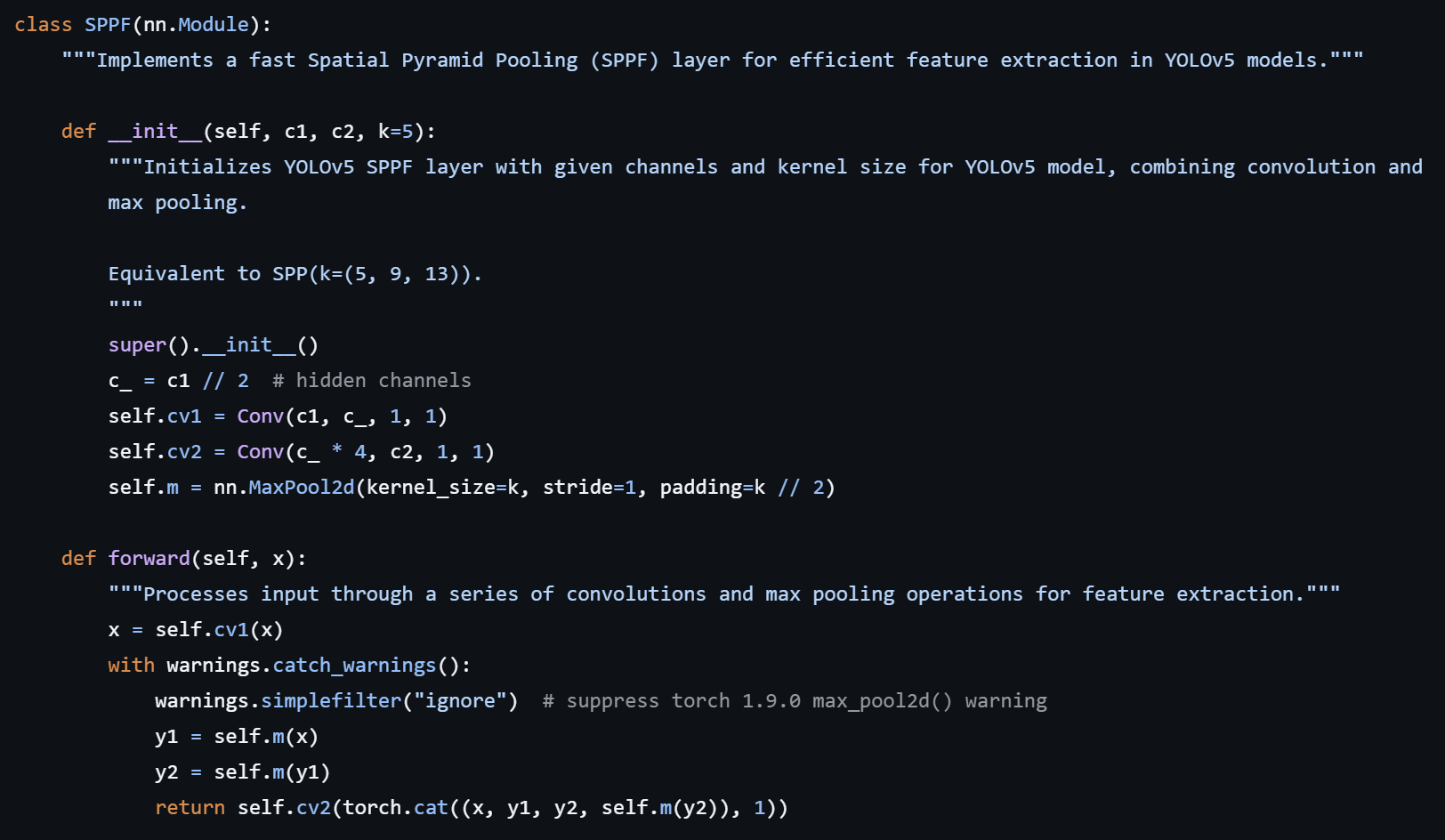
- C3k2 (Cross Stage Partial with kernel size 2) block
- SPPF (Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast)
- C2PSA (Convolutional block with Parallel Spatial Attention) components
을 추가하여 기존의 YOLO에 비해 성능향상을 한 번 더 이뤄냈다
3-1. Architecture

- C3k2는 기존의 C2f block을 대체 : 하나의 large convolution 대신 두 개의 작은 convolution을 통해 성능을 유지하면서 더 빠른 처리를 가능하게 한다.

- SPPF & C2PSA :
Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast : 기존의 feature map을 다양한 크기로 종합하여 가져오는 것은 더 빠르게(수학적으로 동등한 연산을 kernel size를 줄임으로써 더 적은 연산량과 효율적인 메모리 사용을 도달할 수 있음)
C2PSA(Cross Stage Partial w/ Spatial Attention) : Spatial Attention을 가능하게 하여 집중하고싶은 공간정보가 있다면 그 부분에 focus를 맞추는 것이 가능함 - CBS(Convolution-BatchNorm-SiLu) : YOLOv11의 head에 포함된 layer들
- 관련된 특징을 추출하여 더 정확한 object detection을 가능하게 해준다
- Batch Normalization을 통해 data flow를 안정화하고 표준화시킨다.
- Sigmoid Linear Unit (SiLU)를 활용하여 non-linearity를 가져감 - Final Convolution layer and Detect layer : detection branch의 마지막으로 필요한 feature의 개수만큼만 output을 남기면 되기 때문에 이를 조절하여 마지막 Convolution layer를 계산함
- bounding box coordinates
- Objectness score that indicate the presence of objects
- Class scores for determining the class


