End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers (ECCV 2020)
- Nicolas Carion, Francisco Massa, Gabriel Synnaeve, Nicolas Usunier, Alexander Kirillov, and Sergey Zagoruyko (Facebook AI Research)
1. Introduction
- 기존 object detector들은 성능은 뛰어나지만, spacial anchor, IoU threshold, NMS 등 많은 hand-designed components에 의존한다. 이로 인해 파이프라인이 복잡해지고, domain 마다 재설계가 필요하다.
- Hand-designed components 없이, end-to-end로 학습하는 object detector인 DETR(DEtection TRansformer)을 제안한다.
- Object detection을 set prediction task로 재정의한다. (Class, Bounding box) 쌍의 집합을 예측하는 것으로 object detection이 해결된다.
2. Architecture

2.1. Input, Output, Target
- Input: 이미지
- Output: N개의 (class, bounding box) 쌍의 집합(N=100).
- class: object class + background(∅) 각각의 확률분포.
- bounding box: 전체 이미지의 가로, 세로에 대한 비율(0~1)로 표현되는 박스 중심의 x, y좌표, 박스의 가로, 세로 길이.
- Target: M(<N)개의 ground truth (class, bounding box) 쌍과 (N - M)개의 (∅, bounding box) 쌍의 집합
2.2. Loss
- 집합과 집합을 비교하는 문제이기 때문에, 우선 집합의 각 쌍을 대응시켜야 한다.
- Bipartite matching: 각 쌍마다 결정되는 Loss의 합이 최소가 되도록 하는 대응을 찾는다.

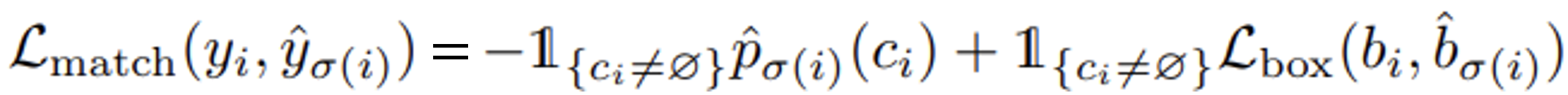
- 이렇게 찾은 대응 σ에 대해, Loss를 다음과 같이 정의한다.

- Bounding box loss는 L1 loss와 GIoU의 가중치 합으로 정의한다.

2.3. Backbone
- 이미지 → feature map (H × W x C) 변환하는 역할
- ResNet-50 / ResNet-101 사용
2.4. Encoder
- feature map(H x W x C) → context vector(HW x d)
- 이미지 전체에 대한 global context modeling
- 픽셀 간 spatial dependency 학습
- Backbone의 채널 수를 hidden state의 dimmension과 맞추기 위해 1x1 convolution을 수행한다. (H x W x C → H x W x d)
- Positional Encoding은 Attention is All You Need(2017)와 동일하다. 2차원이기 때문에, x좌표와 y좌표 각각에 positional encoding(d/2 차원)을 적용하고, concat해 사용한다.
- Encoder 구조 또한 Attention is All You Need(2017)와 동일하다. Multi-head self-attention, feed-forward layer의 반복이다.
2.5. Decoder
- context vector(HW x d) → output embedding(N x d)
- context vector에 담긴 전체 이미지에 대한 정보를 바탕으로, 각 object query를 하나의 object hypothesis로 발전시킨다.
- Non-autoregressive. 각 쿼리를 병렬적으로 처리한다.
- Attention is All You Need(2017)의 decoder와 동일하지만, look-ahead mask를 사용하지 않는다.
- output query, 즉 decoder의 초기 입력을 학습 가능한 파라미터로 설정한다.
2.6. Prediction feed-forward network
- output embedding(N x d) → class label(N x C+1), bounding box(N x 4)
- decoder의 출력을 (class, bounding box)의 집합으로 변환한다.
- Class prediction header와 bounding box prediction header로 구분된다.
- Class prediction header: Linear layer + Softmax
- Bounding box prediction header: 3-layer Perceptron
2.7. Additional techniques
- 안정적인 학습을 위해 auxiliary loss를 사용한다.
- auxiliary loss: 마지막 decoder 출력만이 아니라 모든 decoder layer의 출력에 동일한 detection loss를 걸어 앞쪽 decoder layer에 직접적으로 gradient를 전달한다.
- 각 decoder layer의 출력에 prediction feed-forward network와 같은 header를 붙여 auxiliary loss를 계산한다.
- 대부분의 object query는 background(∅)이기 때문에, 이를 완화하기 위해 background class의 경우 loss에 0.1의 가중치를 곱한다.
3. Experiments
3.1. Comparison with Faster R-CNN and RetinaNet

- 가장 위는 baseline architecture의 결과이다. 가운데는 baseline architecture에 data augumentation, GIoU(General IoU), 그리고 더 많은 training epoch를 적용한 결과이다. 아래가 DETR의 결과이다.
- 큰 크기의 물체에 대해서는 높은 성능을 보여주지만(AP_L), 작은 크기의 물체에 대해서는 성능이 저조하다(AP_S).
- DC5: backbone의 마지막 convolution layer의 stride를 1로 줄이고, diliation을 2로 설정하여 2배 높은 해상도의 feature map을 사용한다.
- FPN: Feature Pyramid Network의 약자로, 서로 다른 scale의, 여러 장의 feature map을 사용한다.
- R101: ResNet-50보다 깊은 ResNet-101을 backbone으로 사용한다.
3.2. Ablation Study

- 6개의 decoder layer를 사용하는 경우 NMS postprocessing에 의한 유의미한 성능 변화가 관찰되지 않았다. Decoder가 깊어질수록 output query 사이의 상호작용이 많아지면서, 같은 물체에 대한 중복된 예측이 일어나지 않는다.
- 훈련 데이터셋에서 기린은 최대 13마리가 한번에 나타남에도 불구하고, 기린이 24마리 있는 이미지에 대해서도 정확하게 인식한다. 이는 각 object query가 특정 클래스에 고정되어 있지 않다는 것을 보여준다.
- Encoder layer, decoder layer, prediction feed-forward layer, positional encoding을 제거 또는 축소했을 때 유의미한 성능 저하가 일어남을 실험적으로 확인했다. 즉 모든 요소가 DETR의 성능에 기여한다.
Deformable DETR: Deformable Transformers for End-to-End Object Detection (ICLR 2021)
- Xizhou_Zhu, Weijie Su, Lewei Lu, Bin Li, Xiaogang Wang, Jifeng Dai
1. Introduction
- DETR은 구조가 간단하고 end-to-end로 학습한다는 장점이 있지만, 학습에 많은 epoch가 필요하고(느리게 수렴함), 작은 물체에 대해 인식 성능이 저조하다.
- 이미지는, 특히 물체 인식에서 sparse한 데이터이다.
- Deformable convolution에서 영감을 얻은 deformable attention을 제안한다.
- IDEA: Attention을 모든 위치에 대해 계산하지 않고, 각 query마다 "소수의 의미 있는 sampling point”만 관찰해도 충분하다.
- Deformable Convolution의 sparse spatial sampling + Transformer의 relation modeling → 빠른 수렴 + 멀티스케일 처리 가능(작은 물체에 대한 인식 성능 향상)
2. Architecture

2.1. Input, Output, Target, Loss
- Input, Output, Target, Loss는 모두 DETR과 동일하다.
- Prediction set의 크기: 100 → 300
2.2. Multiscale Feature Map
- 다양한 해상도의 feature map을 사용해 context를 늘리고, 물체 크기에 상관없이 감지할 수 있도록 한다.
- ResNet의 C3, C4, C5 feature map + C5에 stride가 2인 convolution을 적용한 C6 feature map 4개를 사용한다(Cn: 원래 이미지보다 해상도가 2^n배 낮은 feature map).
2.3. Deformable Attention
- 기존 Transformer Attention: 모든 key 위치를 봄 → 비효율적, 느린 수렴
- Deformable Attention: 각 query마다 K개의 sampling point만 선택

- sampling point 위치는 query feature로부터 얻어지는 offset + reference point로 결정된다.
- 연산량이 spatial size에 선형적이다(기존 Attention은 spatial size의 제곱).
- attention이 처음부터 구조적으로 sparse하기 때문에 빠르게 수렴한다.
- context vector(query) z, reference point p, feature map(key) x에 따라 변화한다.
2.4. Multiscale Deformable Attention
- Deformable Attention을 여러 scale feature map에 동시에 적용한다.
- 각 scale에서 K개씩 sampling → 총 L x K sampling point

- multiscale detection이 가능하다 → 작은 물체의 인식 성능이 높아진다.
- 서로 다른 scale의 feature map끼리 상호작용이 가능하다.
2.5. Encoder
- 기존 DETR encoder의 self-attention을 Multi-scale Deformable Self-Attention으로 대체한 encoder
- Query / Key: 모두 pixel 단위 (각 scale의 feature map)
- Reference point: 각 pixel 자기 자신
- multiscale feature map → multiscale feature map (같은 크기, 같은 해상도)
2.6. Decoder
- self-attention은 기존 DETR decoder와 같은 Transformer self-attention
- 기존 DETR decoder의 cross-attention을 Multi-scale Deformable Cross-Attention로 대체
- Query: 학습 가능한 파라미터
- Key: encoder 마지막 레이어의 multiscale feature map
- Reference point: query의 linear projection
- multiscale feature map → output embedding(N x d)
2.7. Prediction feed-forward network
- 구조는 DETR과 동일하다.
- box를 절대적인 위치가 아니라 reference point에 대한 상대적인 위치로 예측한다.
2.8. Additional techniques
- Iterative bounding box refinement: 이전 layer의 bounding box prediction을 refine해 새로운 bounding box prediction을 얻는다(~Residual connection).
- Reference point: 두 번째 decoder layer부터는 이전 layer의 box center.
- 이전 box center 기준 offset을 예측해 새로운 box prediction을 얻는다.
- Two-stage Deformable DETR: initial object query가 이미지에 dependent한 것이 합리적이다.
- Encoder에서 decoder의 initial object query를 생성한다. Encoder 학습 - decoder 학습의 두 단계로 나뉘게 된다.
3. Experiments
3.1. Comparision of Deformable DETR with DETR

- 같은 epoch를 훈련했을 때 확연한 성능 차이가 나타난다 → 빠르게 수렴한다.
- 10배 적은 epoch로 DETR보다 뛰어난 성능을 기록했다.
- 작은 물체에 대해서도 Faster R-CNN보다 높은 성능을 보인다(AP_S).
- DETR-DC5+: Focal loss, prediction set의 크기가 300으로 Deformable DETR과 동일
3.2. Comparision of Deformable DETR with SOTA methods

- ResNeXt + DCN backbone의 Deformable DETR이 COCO 2017 dataset에서 SOTA 성능을 달성했습니다.
- DCN: Deformable convolution network
- TTA: test-time augumentation
Conclusion
End-to-end 학습의 철학을 object detection으로 가져온 DETR과, deformable attention을 제안해 DETR을 보완하고 SOTA 성능을 달성한 Deformable DETR에 대해 살펴보았습니다.

